|
|
|
| <<
Mar 03| HISTORY
“4” “2”DAY
|Mar 05 >> Events, deaths, births, of MAR 04 [For Mar 04 Julian go to Gregorian date: 1583~1699: Mar 14 — 1700s: Mar 15 — 1800s: Mar 16 — 1900~2099: Mar 17] |
| On a 04 March:
2001 Swiss referendum overwhelmingly rejects a proposal for immediate membership talks with the European Union. 2001 El candidato del Partido Liberal y jefe del gobierno andorrano, Marc Forné Moline, logra la mayoría absoluta en las elecciones legislativas. 1999 Outraging Italian authorities, a military jury in North Carolina cleared a Marine pilot of charges he was flying recklessly when his jet sliced through a ski gondola cable in the Alps, sending 20 people plunging to their deaths. [As usual, the military and police in the US are treated as if they had a license to kill innocent civilians, especially foreigners]. 1999 El proceso de paz en Irlanda queda bloqueado ante la negativa del IRA a entregar las armas. 1998 Microsoft, la compañía liderada por Bill Gates, decide modificar los contratos que obligan a muchos proveedores de Internet a ofrecer en exclusividad el software de navegación fabricado por su empresas.
1997 President Clinton bans federally funded human cloning research, saying that the creation of life is "a miracle that reaches beyond laboratory science." 1995 Blind teenage boy receives a 'Bionic Eye' at a Washington Hospital.
|
1989 Eastern Airlines machinists strike. 1989 Time Inc. and Warner Communications Inc. announced plans to merge into the world's largest media and entertainment conglomerate. 1987 President Reagan addressed the nation on the Iran-Contra affair, acknowledging that his overtures to Iran had "deteriorated" into an arms-for-hostages deal. [No one suggest impeaching him, as he ought to have been] 1985 Virtual ban on leaded gas ordered by EPA 1981 A jury in Salt Lake City convicts Joseph Paul Franklin, an avowed racist, of violating the civil rights of two Black men who were shot to death. 1980 Robert Mugabe's ZANU-PF wins parliamentary election in Zimbabwe. 1979 US Voyager I photo reveals Jupiter's rings 1974 Harold Wilson replaces resigning Ed Heath as British premier. 1972 Libya & USSR signs cooperation treaty 1972 Erhard Keller (Germany) skates world record 1000 meter (1:18.5) |
1968 Pablo Picasso dona al museo que lleva su nombre, en Barcelona, su extraordinaria serie de 45 lienzos inspirada en Las Meninas. de Velázquez. — In 1957, at age 76, Picasso spent four intense months producing 45 variations [one of them] of Velázquez's masterpiece Las Meninas — PICASSO LINKS 1966 North Sea Gas is first pumped ashore by BP 1966 London's "Evening Standard" newspaper published an interview with Beatle John Lennon in which he remarked: 'Christianity will... vanish and shrink... We're more popular than Jesus Christ right now.' The quote touched off a storm of international protest, resulting in burnings and boycotts of the Beatles' records. 1964 Jimmy Hoffa convicted of jury tampering 1962 AEC announces 1st atomic power plant in Antarctica in operation. 1961 Paul-Henri Spaak resigns as Secretary-General of NATO. 1959 El primer ministro soviético Nikita Sergeievich Kruschov anuncia un tratado de paz por separado con la RDA.
1948 Firma del acuerdo chileno-argentino sobre la soberanía de la Antártida, por el que ambos países se comprometen a actuar de común acuerdo en defensa del territorio. 1945 Finland declares war on Nazi-Germany 1944 Anti-Germany strikes in North Italy. 1944 Dimite en Cuba el gobierno de Ramón Zaidyn. El presidente Fulgencio Batista y Zaldívar forma un nuevo gobierno.
|
| 1933 Inaugural
Address of US President Franklin D. Roosevelt (First
Term), in which he says: "We
have nothing to fear but fear itself" ^top^ In the depths of the Great Depression, Franklin Delano Roosevelt is inaugurated as the 32nd president of the United States. In his famous inaugural address, delivered outside the east wing of the US Capitol, Roosevelt outlined his "New Deal"--an expansion of the federal government as an instrument of employment opportunity and welfare--and told Americans that "the only thing we have to fear is fear itself." Although it was a rainy day in Washington, and gusts of rain blew over Roosevelt as he spoke, he delivered a speech that radiated optimism and competence, and a broad majority of Americans united behind their new president and his radical economic proposals to lead the nation out of the Great Depression. Born into an upper-class family in Hyde Park, New York, in 1882, Roosevelt was the fifth cousin of Theodore Roosevelt, who served as the 26th US president from 1901 to 1909. In 1905, Franklin Roosevelt, who was at the time a student at Columbia University Law School, married Anna Eleanor Roosevelt, the niece of Theodore Roosevelt. After three years as a lawyer, he decided to follow his cousin Theodore's lead and sought public office, winning election to the New York State Senate in 1910 as a Democrat. He soon won a reputation as a charismatic politician dedicated to social and economic reform. Roosevelt supported the progressive New Jersey governor Woodrow Wilson in his bid for the Democratic presidential nomination, and after Wilson's election in 1912 Roosevelt was appointed assistant secretary of the US Navy, a post that Theodore Roosevelt once held. In 1920, Roosevelt, who had proved himself a gifted administrator, won the Democratic nomination for vice president on a ticket with James Cox. The Democrats lost in a landslide to Republicans Warren Harding and Calvin Coolidge, and Roosevelt returned to his law practice and undertook several business ventures. In 1921, he was stricken with poliomyelitis, the virus that causes the crippling disease of polio. He spent several years recovering from what was at first nearly total paralysis, and his wife, Eleanor, kept his name alive in Democratic circles. He never fully covered and was forced to use braces or a wheelchair to move around for the rest of his life. In 1924, Roosevelt returned to politics when he nominated New York Governor Alfred E. Smith for the presidency with a rousing speech at the Democratic National Convention. In 1928, he again nominated Smith, and the outgoing New York governor urged Roosevelt to run for his gubernatorial seat. Roosevelt campaigned across the state by automobile and was elected even as the state voted for Republican Herbert Hoover in the presidential election. As governor, Roosevelt worked for tax relief for farmers and in 1930 won a resounding electoral victory just as the economic recession brought on by the October 1929 stock market crash was turning into a major depression. During his second term, Governor Roosevelt mobilized the state government to play an active role in providing relief and spurring economic recovery. His aggressive approach to the economic crisis, coupled with his obvious political abilities, gave him the Democratic presidential nomination in 1932. Roosevelt had no trouble defeating President Herbert Hoover, who many blamed for the Depression, and the governor carried all but six states. During the next four months, the economy continued to decline, and when Roosevelt takes office on 04 March 1933, most banks were closed, farms were suffering, 13 million workers were unemployed, and industrial production stood at just over half its 1929 level. Aided by a Democratic Congress, Roosevelt took prompt, decisive action, and most of his New Deal proposals, such as the Agricultural Adjustment Act, National Industrial Recovery Act, and creation of the Public Works Administration and Tennessee Valley Authority, were approved within his first 100 days in office. Although criticized by many in the business community, Roosevelt's progressive legislation improved America's economic climate, and in 1936 he easily won reelection. During his second term, he became increasingly concerned with German and Japanese aggression and so began a long campaign to awaken America from its isolationist slumber. In 1940, with World War II raging in Europe and the Pacific, Roosevelt agreed to run for an unprecedented third term. Reelected by Americans who valued his strong leadership, he proved a highly effective commander in chief after the December 1941 US entrance into the war. Under Roosevelt's guidance, America became, in his own words, the "great arsenal of democracy" and succeeded in shifting the balance of power in World War II firmly in the Allies' favor. In 1944, with the war not yet won, he was reelected to a fourth term. Three months after his inauguration, while resting at his retreat at Warm Springs, Georgia, Roosevelt died of a massive cerebral hemorrhage at the age of 63. Millions of Americans mourned the death of the man who led the United States through two of the greatest crises of the 20th century: the Great Depression and World War II. Roosevelt's unparalleled 13 years as president led to the passing of the 22nd Amendment to the US Constitution, which limited future presidents to a maximum of two consecutive elected terms in office. |
| 1933 Chancellor Dollfuss disdolves Austrian parliament. 1929 Herbert Hoover inaugurated as 31st President (his Inaugural Address) 1929 Charles Curtis (R-Kans) becomes first native American VP. 1926 De Geer government in Netherlands takes office. 1925 US President Coolidge's inauguration broadcast live on 21 radio stations. (His Inaugural Address) 1925 Swain's Island (near American Samoa) annexed by US. 1924 La Asamblea Nacional Turca, apoyada por el jefe del Estado, Mustafá Kemal “Atatürk”, aprueba la abolición del Califato. 1923 Lenin's last article in Pravda (about Red bureaucracy). 1921 Inaugural Address of US President Warren G. Harding. 1920 Last day of Julian civil calendar in Greece. 1919 Se inaugura en Moscú la Tercera Internacional Comunista, propiciada por la URSS, en la que están representados todos los partidos comunistas en proporción al número de sus afiliados. 1918 Terek Autonomous Republic established in RSFSR (until 1921) 1917 Inaugural Address of US President Woodrow Wilson, Second Term. 1917 Jeannette Rankin (Rep-R-Mont) becomes first female member of Congress 1913 Woodrow Wilson inaugurated for his first term as 28th US President (his Inaugural Address) — Es inaugurado presidente de Estados Unidos Thomas Woodrow Wilson, quien será el autor de los famosos "catorce puntos", base de la paz después de la Primera Guerra Mundial. 1913 US Department of Commerce & Labor split into separate departments 1913 First US law regulating the shooting of migratory birds passed 1911 Victor Berger (Wisconsin) becomes first socialist congressman in US 1909 President Taft sworn-in during 10" snowstorm. 1909 Inaugural Address of US President William Howard Taft 1905 Inaugural Address of US President Theodore Roosevelt [2nd term] 1901 Inaugural Address of US President William McKinley Second Term. 1st advance copy of inaugural speech (Jefferson-National Intelligencer) 1897 William McKinley inaugurated for his first term as 25th President of US (his Inaugural Address) 1893 Grover Cleveland (D) becomes 22nd US president for the 2nd time 1893 Francis Dhanis' army attacksthe Lualaba, occupies Nyangwe 1893 Inaugural Address of US President Grover Cleveland Second Term. 1889 Benjamin Harrison inaugurated as 23rd President (his Inaugural Address) 1885Grover Cleveland inaugrated (first term) as 1st Democratic President since Civil War (his Inaugural Address) 1881 James A Garfield inaugurated as 20th President (his Inaugural Address) 1881 California becomes first state to pass plant quarantine legislation. 1881 South African President Kruger accepts ceasefire 1881 Conand Doyle's characters Sherlock Holmes and Doctor Watson begin A Study in Scarlet, first case together 1876 US Congress decides to impeach Minister of War Belknap 1873 Ulysses S. Grant inaugurated for his 2nd term as 18th President (his Inaugural Address) 1869 Inaugural Address of US President Ulysses S. Grant, First Term. 1865 Inaugural Address of US President Abraham Lincoln Second Term. 1865 Confederate congress approves final design of "official flag" 1863 US President Lincoln signs an act creating Idaho Territory. 1863 Battle of Thompson's Station, Tennessee 1862 Siege of New Madrid, Missouri continues 1861 Abraham Lincoln inaugurated for his first term as 16th US President; 1st time US has 5 former Presidents living. (His Inaugural Address) 1861 Confederate States adopt "Stars and Bars" flag. 1857 Inaugural Address of US President James Buchanan (Democrat) 1853 Inaugural Address of US President Franklin Pierce 1853 William Rufus de Vane King (D) sworn in as 13th US VP 1849 US had no president, Polks term ends on a Sunday, Taylor couldn't be sworn-in until the next day, Sen David Atchison (pres pro tem) term ended 3 March. 1848 Sardinia-Piemonte gets new Constitution. 1845 James Knox Polk inaugrated as 11th President (his Inaugural Address) 1841 William Henry Harrison William Henry Harrison makes the longest US Presidential Inaugural Address: 8578 words, 1 hour and 45 minutes, almost twice as many as any other president. Despite the cold weather, Harrison refuses to wear a coat or hat.. He would die of pneumonia on 04 April 1841. 1837 Martin Van Buren inaugrated as 8th US President (his Inaugural Address) 1835 HMS Beagle moves into Bay of Concepción, with Charles Darwin aboard. 1833 Inaugural Address of US President Andrew Jackson Second Term. 1829 Andrew Jackson inaugurated for his first term as 7th US President (his Inaugural Address). An unruly crowd mobs the White House during the inaugural reception. 1825 John Quincy Adams inaugrated as 6th US President (his Inaugural Address) |
| 1817 Inaugural
Address of US President James Monroe, First Term. 1813 Inaugural Address of US President James Madison, Second Term. 1813 El general español Félix María Calleja del Rey, conde de Calderón, toma posesión del cargo de virrey de México. 1809 Madison becomes first president inaugurated in American-made clothes 1809 Inaugural Address of US President James Madison, First Term. — llega a ser el cuarto presidente de Estados Unidos, cargo en el que permanecerá hasta 1817. 1805 Inaugural Address of US President Thomas Jefferson, Second Term. 1801 Inaugural Address of US President Thomas Jefferson, First Term. He is the first president inaugurated in Washington DC 1798 Catholic women forced to do penance for kindling sabbath fire for Jews. 1797 Inaugural Address of US President John Adams. 1793 French troops conquer Geertruidenberg Netherlands.
1791 Vermont admitted as 14th state (first addition to the 13 former colonies) 1789 George Washington asume el cargo de presidente de los Estados Unidos.
1741 English fleet under Admiral Ogle reaches Cartagena 1699 Jews are expelled from Lubeck Germany 1681 England's King Charles II grants a charter to William Penn for an area of land that later will be Pennsylvania. 1665 English King Charles II declares war on Netherlands 1621 Jakarta, Java renamed Batavia 1611 George Abbot appointed archbishop of Canterbury. 1493 Cristóbal Colón, en La Niña, de vuelta de su primer viaje a América, llega a Lisboa, donde es recibido por el rey de Portugal. 1461 Battle at Towton: Duke Edward of York beats English queen Margaret Edward IV recognized as king of England 1152 Frederik I Barbarossa elected Roman-German king |
1999 Nicholas Lemak, 7, Emily Lemak,
6, and Thomas Lemak, 3, murdered by their mother Marilyn
Lemak (née Morrissey), 44 [photos below], in the Chicago
area. First she fed her children peanut butter laced with her anti-anxiety
medication, then laid them down to sleep and put her hand over their mouths
and pinched their noses to suffocate them. Then she goes downstairs to look
for something to kill herself. According to what she said, she takes some
of her medication and slashes her wrists with a knife, never expecting to
wake up. She wakes up the next morning, looks for the knife to kill herself,
can't find it and eventually calls 911. On 05 September 1985, Marilyn Morrissey
married David Lemak, now an emergency medicine physician. Marilyn Lemak
was a part-time nurse. They are in the process of divorce at the time of
the murders. On 19 December 2001, a jury would find Marilyn Lemak guilty
of murder, rejecting her insanity defense..
|
| 1999 Harry A. Blackmun, 90, Retired Supreme Court Justice
who wrote the infamous 1973 Roe v. Wade decision that legalized
abortion, in Arlington, Va. 1996 A suicide bomber and the 13 he kills blowing himself up outside a Tel Aviv shopping center. It is the fourth such attack in nine days. 1992 Christian K Nelson, 92, inventor (Eskimo Pie) 1986 Henri Knap, 75, Dutch journalist/writer 1983 Hergé [Georges Rémi], 75, Belgian cartoonist (Rin-Tin-Tin) 1978 Chicago Daily News, founded in 1875, publishes last issue 1977: 1541 in earthquake in Romania. 1977 Andrés Caicedo Estela, escritor y cineasta colombiano. 1970 Eurydice, French submarine, explodes. 1966: 64 as Canadian Pacific airliner explodes on landing in Tokyo. 1963 William Carlos Williams, 79, US physician/poet 1960: 100 as French freighter La Coubre explodes in Havana, Cuba. 1958 Albert Kuyle [Lou Kuitenbrouwer], writer (Jesus' Carpet), 1953 Sergei S. Prokofiev, 61, Russian composer (Peter & the wolf) 1948 Antonin Artaud, 51, French poet/actor (Napoleon)
|
 1941: 14 German
sailors as British attack fails to capture Enigma.
^top^
1941: 14 German
sailors as British attack fails to capture Enigma.
^top^The British navy raids a German position off the coast of Norway and inside the Arctic Circle-the Lofoten Islands. The raid, code name Operation Claymore, destroys the armed German trawler Krebs --but fails to achieve its objective, the capture of an Enigma coding machine. The Brits severely damaged the trawler, killed 14 German sailors, took another 25 prisoner, and destroyed the Germans' local stockpile of oil. While the attack boosted British public morale temporarily, the Enigma machine still eluded the British military. The commander of the Krebs, Lieutenant Hans Kupfinger, threw it overboard before he was killed in the raid, but the Brits were able to recover documents that gave clues to the Enigma's workings. British intelligence was able to piece together enough of the German coding system to track German naval activity for about five weeks. During the Second World War, German military and diplomatic communications were encoded using an electro-mechanical tool codenamed "Enigma". This device consisted of three wheels (chosen from a standard set) which were individually wired to change one letter code to another. To further encrypt the message, after each character, the wheels would be incremented (like a car's odometer) so that a different letter code would be produced for repeated characters. Enigma could only encrypt the twenty-six letters of the alphabet (which means all messages had to be in characters with no numbers, blanks or punctuation). A message was encoded using an agreed to (between the transmitter and receiver) set of wheels with specific starting positions. To encrypt the message, the text was simply keyed into the Enigma's keyboard and a light representing the encoded character was lit. Decoding messages was simply done by reversing the order of the wheels and running through the process again. England's ability to decode messages encrypted on "Enigma" machines was characterized as the greatest secret of the Second World War. It was so secret that this capability was unknown outside government circles until the war had been over for thirty years! The reason why "Ultra" (which was the British code name for the decoding effort) was kept secret for so long seems to be motivated by protecting the governments of the time and avoid the embarrassment of having to explain why they allowed the Germans to bomb cities without taking measures to protect civilians. The bombing of Coventry in 1940 was known to Prime Minister Churchill beforehand, who deliberately did not order the evacuation of civilians or the bolstering of anti-aircraft defenses before the raid in fear of tipping off the Germans that they were able to decode their most secret communications. The decoding of the "Enigma" messages by the English was accomplished by knowing parts of messages (such as the transmitting station's call letters) and trying every possible wheel and initial position to find those parts of the message that matched. This was done on a variety of elctro-mechanical computing "engines" which were design to run through different combinations as quickly as possible to find the known clear-text parts of the messages. On average, it took six months of effort (with early computers) to "break" one wheel selection and settings. Over the course of the war, the Germans specified several thousand different wheel selections and settings. In this time period (from 1938 to 1945), the British decoded approximately 50'000 messages, of the average 2000 intercepted each day. Codebreakers in Poland had started working on the Enigma before the German invasion as well as during the occupation. The Americans used their "Magic" program to decode Japanese diplomatic codes (which were used for military communications). The Americans took a different tack from the British and developed decrypting engines based on standard phone switching equipment (the English engines used custom hardware). The American's "engines" were much cheaper, faster and more reliable than their UK counterparts. |
| 1940
Day 97 of Winter War: USSR aggression against Finland. ^top^ More deaths due to Stalin's desire to grab Finnish territory. Kollaa still holding out! Heavy fighting also in Vuosalmi and Gulf of Viborg Ladoga Karelia: Kollaa is still holding out! The 69th Infantry Regiment is holding its ground in the face of the massive Red Army offensive in Kollaa. Artillery shelling and patrol activities nevertheless continue. On the Isthmus, a Soviet assault launched at 6 o'clock in the morning leads by nightfall to the capture of a bridgehead near Äyräpää church. Around noon Russian troops supported by tanks once again come ashore at Vilajoki and Häränpäänniemi on Viipurinlahti bay. What little air power Finland has is concentrated to resist the enemy offensive across Viipurinlahti bay. Detachment Alfthan unsuccessfully attempts to take Lavajärvi village. The enemy threatens Kotka and Virolahti. A new combat detachment, Detachment Aarnio, is being formed to fight along the section of the front between Mustalampi and Lavajärvi with the task of cutting the enemy's supply lines. President Kyösti Kallio congratulates Commander-in-Chief Mannerheim on the destruction of a Russian tank brigade. Soviet military command in Leningrad denies bombing Finnish towns and villages and accuses the Finns of provocation. A crash between a goods train carrying children and an express train at Iittala, near Hämeenlinna, claims 31 lives; 11 of the dead are children. Abroad: today is Finnish day at the Holmenkollen games in Oslo. In a speech at Holmenkollen, the Finnish speedskater Clas Thunberg says: "My people hope that here in Norway you will realise that Finland's cause is also your cause. The Finns dying at the front are giving their lives to protect all of us in the Nordic countries." Thunberg's speech is followed by a rendering of the Finnish national anthem. Kollaa kestää! Talvisodan 96. päivä, 04.maaliskuuta.1940 ^top^ Kollaa kestää! Kollaalla JR 69 torjuu puna-armeijan suurhyökkäyksen. Tykkituli ja partiointi jatkuvat. Klo 06.00 alkaa neuvostohyökkäys, jonka vuoksi iltaan mennessä viholliselle menetetään sillanpää Äyräpään kirkon maastossa. Noin klo 12 panssareiden tukemat venäläisjoukot nousevat uudelleen maihin Viipurinlahden Vilajoella ja Häränpäänniemessä. Suomen vähäiset ilmavoimat keskitetään torjumaan vihollisen hyökkäystä Viipurinlahden yli. Osasto Alfthanin yritys vallata Lavajärven kylä epäonnistuu. Vihollinen uhkaa Kotkaa ja Virolahtea. Mustalammen ja Lavajärven välisen rintamanosan taisteluja käymään muodostetaan taisteluosasto Aarnio, jonka tehtäväksi määrätään vihollisen huoltotien katkaisu. Tasavallan Presidentti Kyösti Kallio osoittaa ylipäällikkö Mannerheimillekiitoksen hyökkäysvaunuprikaatin tuhoamisen johdosta. Leningradin sotilasjohto kiistää suomalaisten kaupunkien ja kylien pommittamisen syyttäen suomalaisia provokaatiosta. Iittalassa tapahtuu tuhoisa junaonnettomuus lapsia kuljettavan tavarajunan ja pikajunan törmätessä toisiinsa. Yhteentörmäyksessä kuolee 31 henkeä, joista 11 on lapsia. Ulkomailta: Holmenkollenin kisoissa vietetään tänään Suomen päivää. Pikaluistelija Clas Thunberg sanoi puheessaan Holmenkollenilla:"Kansani pyytää, että te täällä Norjassa oivallatte Suomen asian omaksi asiaksenne. Rintamalla kaatuvat suomalaiset kaatuvat Pohjolan puolesta." Thunbergin puheen jälkeen tilaisuudessa kuultiin Maamme-laulu. Kollaa håller! Vinterkrigets 96 dag, den 04 mars 1940 ^top^ Kollaa håller! JR 69 slår tillbaka Röda Arméns anstormning i Kollaa. Artillerield och patrullering fortsätter. Kl. 06.00 börjar en rysk offensiv som leder till att brohuvudet i terrängen kring Äyräpää kyrka går förlorad på kvällen. Ungefär kl. 12 stiger ryska trupper igen i land i Vilajoki och Häränpäänniemi i Viborgska viken. Finlands fåtaliga luftvapen koncentreras för att avvärja fiendens anfall över Viborgska viken. Avdelning Alfthan försöker erövra byn Lavajärvi men misslyckas. Fienden hotar Kotka och Vederlax. Stridsavdelning Aarnio bildas för att kämpa på frontavsnittet mellan Mustalampi och Lavajärvi. Avdelningens uppgift är att skära av fiendens försörjningsled. Republikens president Kyösti Kallio riktar ett tack till överbefälhavare Mannerheim för förintelsen av en stridsvagnsbrigad. Den militära ledningen i Leningrad förnekar bombningen av finska städer och byar, och beskyller finnarna för provokation. I Iittala sker en förödande tågolycka när ett godståg som transporterar barn och ett snälltåg kolliderar. Vid kollisionen omkommer 31 personer varav 11 är barn. Utrikes: Vid tävlingarna i Holmenkollen firar man idag Finlands dag. Skridskoåkaren Clas Thunberg sade i sitt tal i Holmenkollen:"Mitt folk ber att ni här i Norge tar er an Finlands sak. De soldater som stupar på fronten stupar för hela Norden." Efter Thunbergs tal följde hymnen Vårt land. |
| 1927 Solomon
Cicurel, 46, stabbed 8 times, shortly after midnight, in his
Cairo mansion. The murder of the wealthy Jewish merchant is the crime of
the year in Egypt. 1926 Pedro Morales Pino, músico y pintor colombiano. 1921 William Anderson, innocent Black, lynched in Baker County, Georgia, after been mistaken for a Black suspected of a crime. 1919 Georges Jules Auguste Caïn, French artist born on 14 April 1856. 1916 Franz Marc, born on 08 February 1880, German Expressionist painter, specialized in Animals, is killed fighting in WW I, near Verdun. — MORE ON MARC AT ART “4” MARCH — LINKS — Dog Lying in the Snow 1913 Edouard Frédéric Wilhelm Richter, French artist born on 13 June 1844. 1903 Joseph H. Shorthouse, 68, English writer (John Inglesant) 1908: 180 in fire of Collingwood OH primary school. 1906 Cuatro mil muertos en México por el tifus. 1894 Great fire in Shanghai; over 1000 buildings destroyed. 1888 Amos Bronson Alcott, 88, US theory / poet (Table Talk), author of Ralph Waldo Emerson: An Estimate of his Character and Genius: in Prose and Verse — Ralph Waldo Emerson: An Estimate of his Character and Genius: in Prose and Verse — Sonnets and Canzonets 1883 Alexander H Stephens, 71, Vice President Confederate States 1875 Gottfried Johan Pulian, German artist born on 27 July 1809. 1872 Cornelius David Krieghoff, Dutch Canadian painter born on 19 June 1815. — LINKS
1832 Jean-François Champollion, egiptólogo francés. 1811 Mariano Moreno, político argentino miembro de la primera Junta de Buenos Aires, fallece en viaje hacia Inglaterra por el Atlántico.
1794 Henri D. comte de Larochejacquelin, 21, French Royalist Army leader. 1793 Isaak Ouwater, Dutch artist born on 16 March 1750. 1793 Frans Anton Zeiller, Austrian artist born on 03 May 1716. 1776 Johann Gerg Ziesenis, Danish artist born in 1716. 1766 Jacques-André-Joseph Camelot Aved (or Avet) “le Batave”, French painter specialized in portraits born on 12 January 1702. — LINKS — Madame Crozat 1761 Jacques-François Delyen (or Delien, Deslyens), French painter born in 1684. — LINKS — Portrait of a Man 1700 Lorenzo Pasinelli, Italian artist born on 04 September 1629. — MORE ON PASINELLI AT ART “4” MARCH — Amore disarmato dalle ninfe di Diana — Fanciulla con gabbietta vuota 1615 Hans von Aachen, German painter
1484 Kazimierz the Saint, 25, Polish ruler/saint.
|
|||||||
| Births which
occurred on a March 04: 1977 First CRAY 1 supercomputer shipped, to Los Alamos Laboratories, New Mexico 1954 Irina Ratushinskaya, USSR, poet (Grey is the color of hope)
1942 El extranjero, de Albert Camus, se publica. 1936 Hindenburg dirigible, first flight, Germany. 1934 Jane van Lawick-Goodall, ethnologist/chimp expert (1974 Walker Prize) 1930 Coolidge Dam in Arizona dedicated 1928 Alan Sillitoe, Nottingham Nottinghamshire England, writer (Loneliness of the Long Distance Runner) 1923 Patrick Moore, England, astronomer/writer (A-Z of Astronomy) 1916 Giorgio Bassani, Italian writer (Botteghe Oscure) 1915 Petrus de Jong, Dutch premier (KVP, 1967-71)
1904 George Gamow, Russian-born US nuclear physicist/cosmologist/writer (1, 2, 3...ìnfinity). He died on 19 August 1968.
 1901
Jean-Joseph Rabéarivelo, Monegasque poet (Enfants d'Orphée) 1901
Jean-Joseph Rabéarivelo, Monegasque poet (Enfants d'Orphée)1898 Georges Dumézil, à Paris, mythologue. 1889 Jean-Gabriel Domergue, French artist who died in 1962. 1889 Francisco Asorey, escultor español. 1887 Test run of first Daimler car. ^top^ The Daimler “benzin motor carriage” [photo >] makes its first test run in Esslingen and Cannstatt, Germany. It is Gottlieb Daimler’s first four-wheel motor vehicle. The “benzin” has nothing to do with Carl Benz; at that time Gottlieb Daimler was Carl Benz’s major competitor. Daimler, an engineer whose passion was the engine itself, had created and patented the first gasoline-powered, water-cooled, internal combustion engine in 1885. In Daimler’s engine, water circulated around the engine block, preventing the engine from overheating. The same system is used in most of today’s automobiles. Daimler’s first four-wheel motor vehicle had a one-cylinder engine and a top speed of 16 km/h. By 1899, Daimler’s German competitor, Benz and Company, had become the world’s largest car manufacturer. In the same year, a wealthy Austrian businessman named Emile Jellinek saw a Daimler Phoenix win a race in Nice, France. So impressed was he with Daimler’s car that he offered to buy thirty-six vehicles from Daimler should he create a more powerful model, but requested that the car be named after his daughter, Mercedes. Gottlieb Daimler would never see the result of his business deal with Jellinek, but his corporation would climb to great heights without him. The Mercedes began a revolution in the car manufacturing industry. The new car was lower to the ground than other vehicles of its time, and it possessed a wider wheelbase for improved cornering. It had four speeds, including reverse, and it reached a top speed of 75 km/h. The first Mercedes had a four-cylinder engine and is generally considered the first modern car. 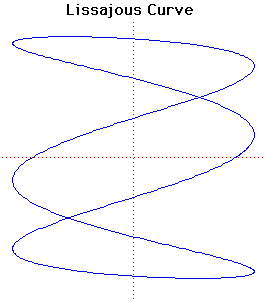 In the year of its birth, the Mercedes set a world speed record of 79.5
km/h in Nice, France--the very course that was responsible for its marquee’s
conception. By 1905, Mercedes cars had reached speeds of 175 km/h. Forever
reluctant to enter car racing, Carl Benz realized he must compete with Daimler’s
Mercedes to preserve his company’s standing in the automotive industry.
For twenty years, Mercedes and Benz competed on racetracks around the world.
In 1926, the Daimler and Benz corporations merged. The two founders never
met.
In the year of its birth, the Mercedes set a world speed record of 79.5
km/h in Nice, France--the very course that was responsible for its marquee’s
conception. By 1905, Mercedes cars had reached speeds of 175 km/h. Forever
reluctant to enter car racing, Carl Benz realized he must compete with Daimler’s
Mercedes to preserve his company’s standing in the automotive industry.
For twenty years, Mercedes and Benz competed on racetracks around the world.
In 1926, the Daimler and Benz corporations merged. The two founders never
met.
1879 Bernhard Kellermann, writer. 1875 Enrique Rodríguez Larreta, Argentine novelist and politician who died on 07 July 1961. 1871 Galerkin, mathematician. 1869 Eugénio de Castro, poeta y escritor portugués. 1866 Eugène Cosserat, mathematician. 1864 Alejandro Lerroux García, político español. 1859 Aleksandr Popov, Russian physicist and electrical engineer who died on 31 December 1905. 1844 Josip Jurcic, Slovenian writer (10th Brother) 1841 Kristian Mandrup Elster, Norwegian author (And fremmed Fugl) 1841 Peter Moran, US artist who died on 10 November 1914. 1837 Chicago is granted a city charter by the Illinois state legislature. 1835 Giovanni Schiaparelli Italy, astronomer (“discovered” canals of Mars) 1826 Granite Railway, 1st US RR chartered, in Quincy MA 1822 Jules Lissajous, mathematician. ^top^ Lissajous was interested in waves and developed an optical method for studying vibrations. At first he studied waves produced by a tuning fork in contact with water. In 1855 he described a way of studying acoustic vibrations by reflecting a light beam from a mirror attached to a vibrating object onto a screen. Duhamel had tried to demonstrate these vibrations with a mechanical linkage but Lissajous wanted to avoid the problems caused by the linkage. He obtained Lissajous figures [Parametric Cartesian equation: x = a sin(nt + c), y = b sin(t) >] by successively reflecting light from mirrors on two tuning forks vibrating at right angles. The curves are only seen because of persistence of vision in the human eye. Lissajous studied beats seen when his tuning forks had slightly different frequencies, in this case a rotating ellipse is seen. 1813 Jan Bedys Tom, Dutch artist who died on 18 July 1894. 1813 Wijnand Jan Josephus Nuyen, Dutch painter specialized in Landscapes who died on 02 June 1839. — LINKS — Ships in a French harbor at low tide (1836) — Shipwreck on a Rocky Coast 1804 The British and Foreign Bible Society (BFBS) ^top^ It is founded at a large interdenominational meeting in London. Its purpose was "to promote the circulation of the Holy Scriptures, without note or comment, both at home and in foreign lands." It is the first Bible society in the fullest sense, founded at the urging of Thomas Charles and members of the Clapham sect, who proposed the idea to the Religious Tract Society in London. An interdenominational Protestant lay society with international representatives in London, the British and Foreign Bible Society was mainly concerned with making vernacular translations of the Scriptures available to peoples of all races at a price they could afford to pay. It also offered financial assistance to Bible societies in other countries. The BFBS has on occasion divided territory with the American Bible Society. 1789 Pavel P. Gagarin, Russian monarch. 1786 Agustina de Zaragoza y Doménech, más conocida como Agustina de Aragón. 1782 Johann Rudolf Wyss, in Bern, folklorist, editor, and writer, remembered for his collections of Swiss folklore and for his completion and editing of his father's novel Der Schweizerische Robinson (Swiss Family Robinson — Swiss Family Robinson in English translation). He died on 21 March 1830. 1775 Giovanni-Battista Lampi II, Alto Adige (South Tyrol) painter who died in 1837.
1749 Caroline-Friederike Friedrich, German artist who died on 20 January 1815. 1747 Casimir Pulaski Count/American Revolutionary War general. 1710 Aert Schouman, Dutch artist who died on 07 May 1792. 1678 Antonio Vivaldi Venice, Baroque violin virtuoso/composer (4 Seasons). He died on 28 July 1741. 1623 Jacob van der Does I “Tambour”, Dutch artist who died on 07 November 1673. 1394 Prince Henry the Navigator, grew up to sponsor Portuguese voyages of discovery. He died on 13 November 1460. |